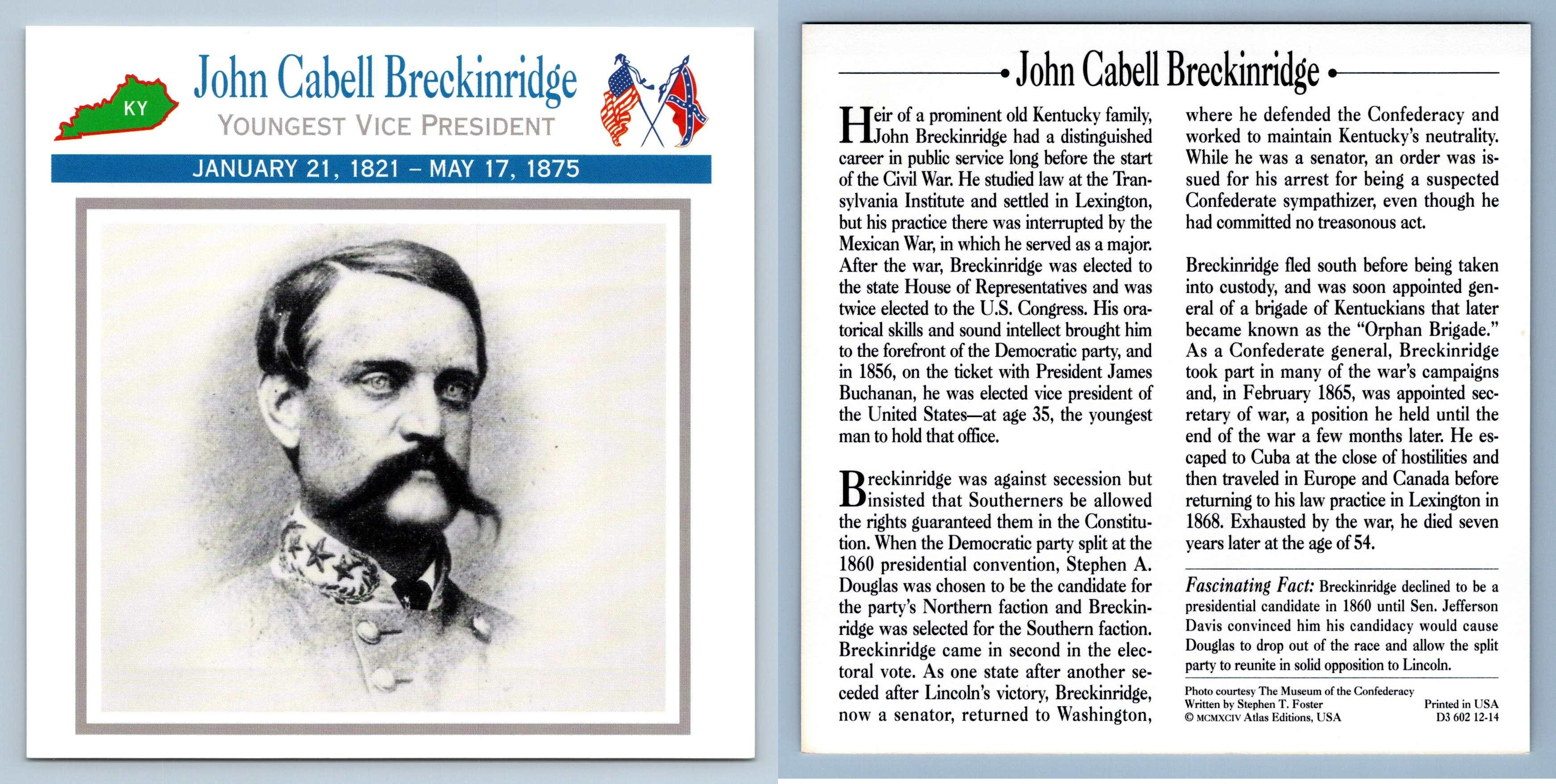
History buffs and political enthusiasts often wonder about the youngest US Vice President and their impact on American politics. The question of "who was the youngest US Vice President" sheds light on a fascinating chapter in U.S. political history. Understanding this role requires delving into the leadership qualities, historical context, and legacy of the individuals who have held this prestigious position.
The Vice Presidency of the United States is more than just a ceremonial role; it is a position of immense responsibility and influence. The individuals who have served in this capacity have contributed significantly to shaping the nation's political landscape. In this article, we will explore the life and achievements of the youngest Vice President, as well as the broader implications of their tenure.
Join us as we uncover the details of this significant historical figure, including their early life, political career, and the challenges they faced. This article will also provide a deeper understanding of the Vice Presidency's evolving role in American governance.
Read also:Gary Anderson And Christina El Moussa Photos A Closer Look At Their Journey
Table of Contents
- Biography of the Youngest US Vice President
- Historical Context of the Vice Presidency
- Early Life and Education
- Political Career Before the Vice Presidency
- Election and Term as Vice President
- Contributions to American Politics
- Challenges Faced During Tenure
- Legacy and Impact
- Comparison with Other Young Leaders
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Biography of the Youngest US Vice President
Key Facts and Data
The youngest US Vice President was John C. Calhoun, who assumed the office at the age of 41. Below is a brief overview of his life and career:
| Full Name | John Caldwell Calhoun |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | March 18, 1782 |
| Place of Birth | Abbeville District, South Carolina |
| Date of Death | March 31, 1850 |
| Profession | Politician, Statesman |
| Political Party | Democratic-Republican, Democratic |
John C. Calhoun's life was marked by a deep commitment to public service and a strong belief in states' rights. His early education and political career laid the groundwork for his future role as Vice President.
Historical Context of the Vice Presidency
Understanding the role of the Vice President requires an appreciation of its historical evolution. Initially viewed as a secondary position, the Vice Presidency has grown in importance over the years. The Constitution assigns the Vice President two primary duties: presiding over the Senate and assuming the presidency in the event of a vacancy.
Calhoun's tenure as Vice President occurred during a transformative period in American history. The early 19th century was marked by debates over slavery, economic policies, and the balance of power between federal and state governments. These issues shaped the political landscape and influenced Calhoun's approach to leadership.
Early Life and Education
John C. Calhoun was born into a family of Scottish-Irish descent in the Abbeville District of South Carolina. His early years were spent in a rural environment, where he developed a strong work ethic and a passion for learning. Despite limited resources, Calhoun's parents prioritized education, sending him to a local academy and later to Yale College, where he excelled academically.
After graduating from Yale, Calhoun studied law at the Litchfield Law School in Connecticut. His legal education provided him with the skills and knowledge necessary to pursue a career in public service. By the early 1800s, Calhoun had established himself as a respected lawyer and politician in South Carolina.
Read also:Navigate To Jfk Airport Your Ultimate Guide To A Seamless Travel Experience
Political Career Before the Vice Presidency
Early Political Achievements
Calhoun's political career began in the South Carolina House of Representatives, where he quickly gained a reputation for his eloquence and intellect. He was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1811, where he became a vocal advocate for national defense and economic development.
- Served as a member of the War Hawks, advocating for the War of 1812.
- Championed the establishment of the Second Bank of the United States.
- Played a key role in drafting the Tariff of 1816.
Calhoun's leadership qualities and policy expertise earned him a promotion to Secretary of War under President James Monroe. During his tenure, he oversaw significant military reforms and infrastructure projects, further solidifying his reputation as a capable administrator.
Election and Term as Vice President
Calhoun was elected as Vice President in 1824 under President John Quincy Adams. At the age of 41, he became the youngest person to hold the office at that time. His term was marked by both achievements and challenges, as he navigated complex political dynamics and personal disagreements with the President.
In 1828, Calhoun was re-elected as Vice President under Andrew Jackson, making him the only person in U.S. history to serve under two different presidents. This unique position allowed him to influence policy across administrations, although his relationship with Jackson was often strained.
Contributions to American Politics
Key Policies and Initiatives
Calhoun's contributions to American politics extended beyond his role as Vice President. He was a staunch advocate for states' rights and the doctrine of nullification, which argued that states had the authority to reject federal laws deemed unconstitutional. While controversial, these ideas had a lasting impact on American jurisprudence and political thought.
- Wrote the "South Carolina Exposition and Protest," outlining the principles of nullification.
- Championed the concept of concurrent majority, emphasizing the need for minority voices in governance.
- Influenced debates on tariffs, slavery, and federal authority.
Calhoun's writings and speeches continue to be studied by historians and political scientists, offering insights into the complexities of 19th-century American politics.
Challenges Faced During Tenure
Calhoun's tenure as Vice President was not without challenges. He faced personal and political conflicts, including:
- A strained relationship with President Andrew Jackson, leading to his eventual resignation.
- Intense criticism from opponents who viewed his states' rights advocacy as a threat to national unity.
- The complexities of balancing regional interests with federal authority during a period of rapid expansion and change.
Despite these challenges, Calhoun remained committed to his principles and continued to influence American politics long after his time in office.
Legacy and Impact
John C. Calhoun's legacy is complex and multifaceted. While his advocacy for states' rights and nullification remains controversial, his contributions to American political thought cannot be ignored. He played a pivotal role in shaping the debates over federalism, slavery, and economic policy that defined 19th-century America.
Calhoun's influence extended beyond his lifetime, as his ideas were invoked by both supporters and critics of the Confederacy during the Civil War era. Modern scholars continue to study his work, recognizing the enduring relevance of his arguments in contemporary discussions about governance and individual liberty.
Comparison with Other Young Leaders
Calhoun's status as the youngest US Vice President places him in an elite group of young leaders who have made significant contributions to American history. Comparisons with figures such as Theodore Roosevelt, who became the youngest President at 42, highlight the importance of youth and energy in political leadership.
While each leader faced unique challenges, their shared characteristic of early achievement underscores the potential for young individuals to make lasting impacts on the nation. Calhoun's legacy serves as a reminder that age is not a barrier to leadership, provided one possesses the necessary expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, John C. Calhoun's tenure as the youngest US Vice President represents a pivotal moment in American political history. His life and career exemplify the complexities of leadership during a transformative period in the nation's development. Key takeaways from this article include:
- Calhoun's early life and education laid the foundation for his future success in public service.
- His contributions to American politics, particularly in the areas of states' rights and federalism, continue to influence contemporary debates.
- The challenges he faced during his tenure highlight the importance of resilience and principled leadership in navigating complex political environments.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments below. For further reading, explore our other articles on American history and political leadership. Together, let's continue the conversation about the individuals and ideas that have shaped our nation's story.