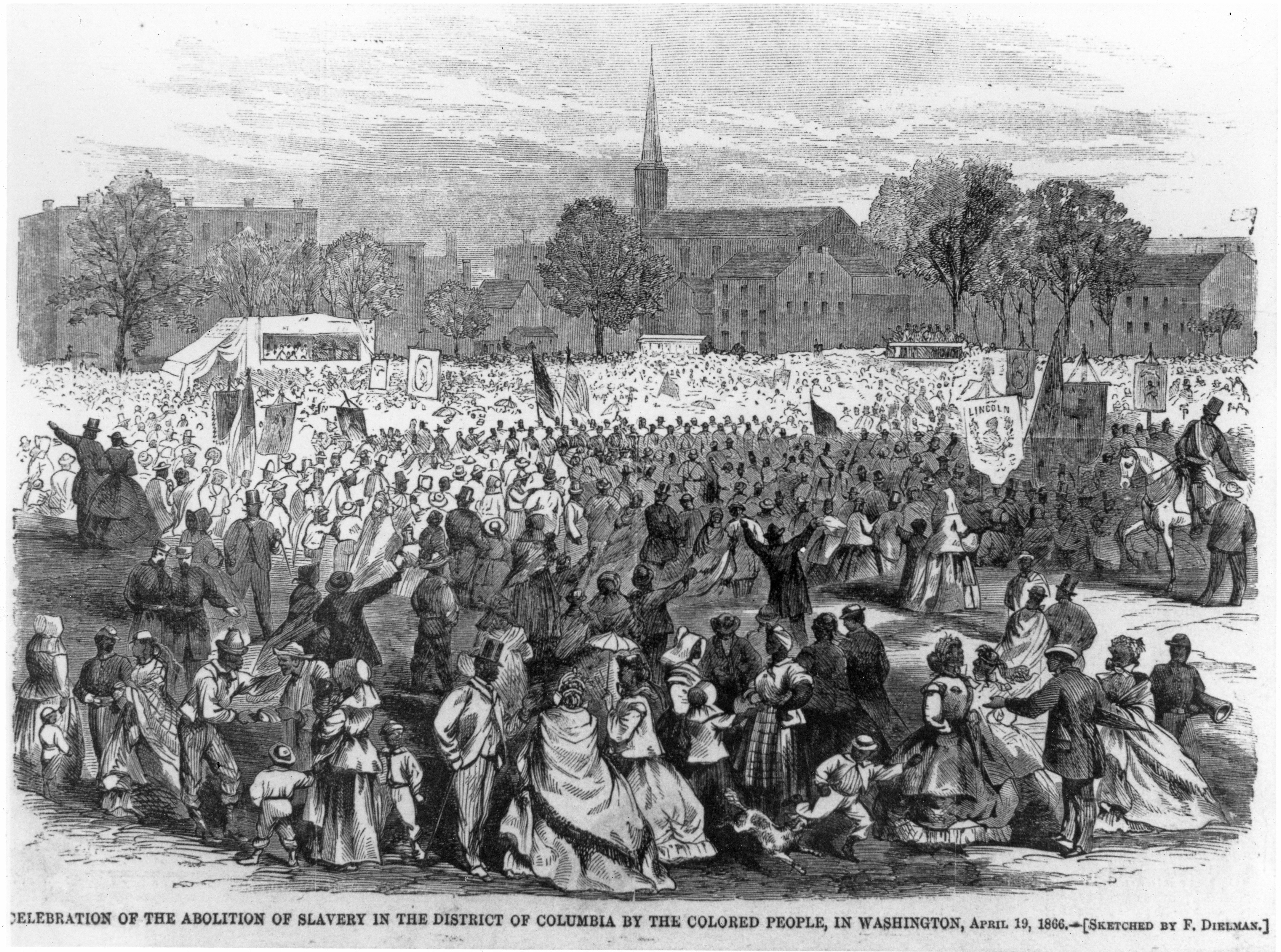Slavery is one of the darkest chapters in human history, and understanding when it was abolished is crucial to appreciating the progress humanity has made toward equality and justice. The abolition of slavery marked a turning point in global history, signifying the end of a brutal institution that had existed for centuries. This article delves into the timeline, events, and key figures that contributed to the eradication of slavery, while also exploring its lasting impact on society today.
Slavery has existed in various forms throughout human history, but its abolition was a significant milestone that reshaped societies around the world. The journey toward ending slavery was not a straightforward one; it involved decades of activism, legislative battles, and social movements. Understanding the history of slavery's abolition requires examining the legal, cultural, and political factors that led to its eventual demise.
As we explore this topic, we will uncover the dates, laws, and individuals who played pivotal roles in abolishing slavery. By examining the global context and the specific events that brought about change, we can gain a deeper appreciation of the struggles faced by those who fought for freedom and equality. Let's take a closer look at when slavery was abolished and what it means for us today.
Read also:Dany Garcia Wedding A Comprehensive Guide To The Starstudded Event
Table of Contents:
- Biography of Key Figures
- Abolition of Slavery in the United States
- Global Abolition of Slavery
- Key Laws and Legislation
- Social Impact of Abolition
- Economic Effects of Abolition
- Resistance to Abolition
- Legacy of Abolition
- Modern Slavery and Human Trafficking
- Conclusion
Biography of Key Figures
The abolition of slavery was driven by individuals who dedicated their lives to fighting for freedom and equality. Below is a brief biography of some of the key figures who played crucial roles in ending slavery:
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, is often credited with leading the effort to abolish slavery in America. His Emancipation Proclamation in 1863 declared that all enslaved people in Confederate-held territory were to be set free. Although the Proclamation did not immediately end slavery, it laid the groundwork for the 13th Amendment, which formally abolished slavery in the U.S. in 1865.
| Name | Birth | Death | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abraham Lincoln | February 12, 1809 | April 15, 1865 | 16th President of the United States |
William Wilberforce
William Wilberforce was a British politician and a leader in the movement to abolish the slave trade in the British Empire. His tireless efforts culminated in the passage of the Slave Trade Act in 1807, which ended the transatlantic slave trade. Wilberforce's work inspired similar movements across the globe.
Abolition of Slavery in the United States
The abolition of slavery in the United States was a complex and tumultuous process that spanned several decades. Below are some key milestones:
Emancipation Proclamation
On January 1, 1863, President Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which declared that all enslaved people in Confederate-held territory were to be set free. Although the Proclamation did not apply to all enslaved individuals, it marked a significant step toward ending slavery in the U.S.
Read also:The Black Dahlia Crime Pictures A Gripping Look Into One Of Americarsquos Most Infamous Murders
13th Amendment
The 13th Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified on December 6, 1865, formally abolished slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. This amendment was a monumental achievement in the fight for civil rights and equality.
Global Abolition of Slavery
The abolition of slavery was not confined to the United States; it was a global movement that affected many countries and regions. Below are some notable dates and events:
Abolition in the British Empire
The British Empire abolished slavery in 1833 with the passage of the Slavery Abolition Act, which took effect in 1834. This legislation ended slavery in most British colonies, freeing over 800,000 enslaved people.
Abolition in Brazil
Brazil was one of the last countries in the Western Hemisphere to abolish slavery. On May 13, 1888, the Golden Law was signed, ending slavery in Brazil. This marked the end of the transatlantic slave trade in the Americas.
Key Laws and Legislation
Several key laws and legislative acts were instrumental in abolishing slavery. Below are some of the most significant:
- Slave Trade Act (1807): Abolished the transatlantic slave trade in the British Empire.
- Emancipation Proclamation (1863): Declared the freedom of enslaved people in Confederate-held territory in the U.S.
- 13th Amendment (1865): Formally abolished slavery in the United States.
Social Impact of Abolition
The abolition of slavery had profound social implications that continue to shape societies today. Below are some of the key social impacts:
Freedom and Equality
The abolition of slavery marked a significant step toward achieving freedom and equality for millions of people. It paved the way for civil rights movements and inspired future generations to fight for justice.
Cultural Changes
Abolition led to significant cultural changes, as formerly enslaved individuals sought to rebuild their lives and communities. This period saw the rise of new cultural expressions, including art, music, and literature.
Economic Effects of Abolition
The abolition of slavery also had significant economic consequences, both positive and negative. Below are some key points:
- Loss of Labor Force: Many plantation owners faced economic challenges as they lost access to free labor.
- New Economic Opportunities: Abolition opened up new economic opportunities for formerly enslaved individuals, who could now pursue education and entrepreneurship.
Resistance to Abolition
Despite widespread support for abolition, there were significant pockets of resistance. Below are some examples:
Political Opposition
Some politicians and business leaders opposed abolition, arguing that it would harm the economy and disrupt traditional ways of life. This resistance often led to intense debates and conflicts.
Cultural Resistance
Cultural attitudes toward slavery were deeply ingrained in some societies, making it difficult to change perceptions overnight. Education and advocacy played crucial roles in overcoming this resistance.
Legacy of Abolition
The legacy of abolition continues to influence societies around the world. Below are some key aspects of this legacy:
Human Rights Movements
The abolition of slavery inspired future human rights movements, including the civil rights movement in the United States and global efforts to combat modern slavery.
Education and Awareness
Education remains a powerful tool in raising awareness about the history of slavery and its ongoing effects. Museums, memorials, and educational programs help ensure that this history is not forgotten.
Modern Slavery and Human Trafficking
While slavery was officially abolished in many parts of the world, modern forms of slavery and human trafficking persist today. Below are some key facts:
Global Statistics
According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), approximately 25 million people are victims of forced labor and human trafficking worldwide. This highlights the need for continued efforts to combat modern slavery.
Prevention and Awareness
Governments, NGOs, and international organizations are working together to prevent modern slavery and raise awareness about its dangers. Education and policy reform are essential components of these efforts.
Conclusion
The abolition of slavery was a monumental achievement in human history, marking the end of a brutal institution that had existed for centuries. From the Emancipation Proclamation in the United States to the Slavery Abolition Act in the British Empire, key laws and individuals played crucial roles in bringing about change. However, the fight against slavery is not over; modern forms of slavery and human trafficking continue to affect millions of people worldwide.
We invite you to reflect on this history and consider how you can contribute to the ongoing struggle for justice and equality. Leave a comment below, share this article with your network, or explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of this important topic.