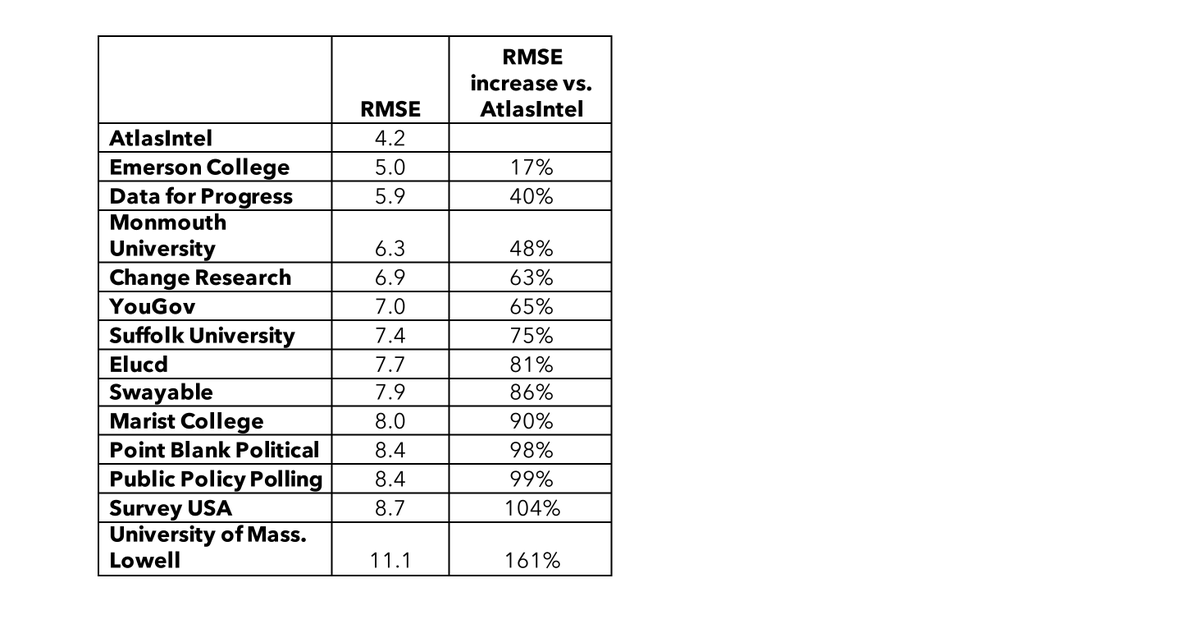
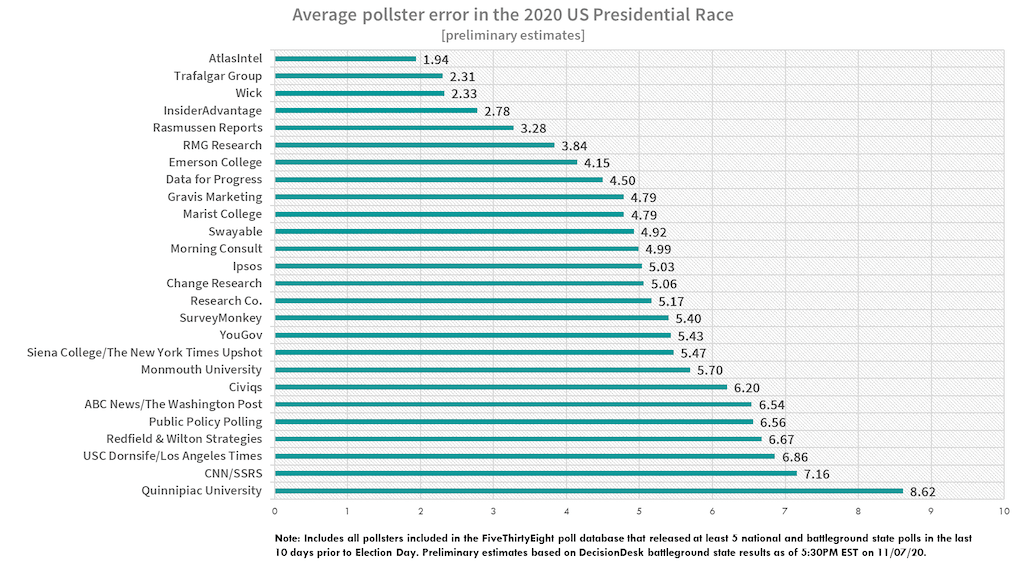
Polling has become an integral part of modern decision-making, influencing everything from political elections to business strategies. However, the accuracy of polling results often faces challenges due to various factors, one of which is polling bias. Understanding polling bias is crucial for interpreting data correctly and making informed decisions. In this article, we will explore the concept of atlas intel polling bias, its types, causes, and how it affects the reliability of polling data.
Polling bias can skew results, leading to incorrect conclusions and potentially harmful decisions. Whether you're a researcher, a business professional, or a curious individual, understanding the nuances of polling bias is essential. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of atlas intel polling bias, offering insights into its mechanisms and implications.
By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how polling bias works, its impact on data accuracy, and strategies to mitigate its effects. Let's delve into the world of polling and uncover the hidden biases that may affect the decisions we make every day.
Read also:When Did Magic Get Drafted A Comprehensive Guide To Magic Johnsons Nba Journey
What is Polling Bias?
Polling bias refers to any systematic error or distortion in polling data that leads to inaccurate representation of public opinion or behavior. This bias can arise from various sources, including sampling errors, question wording, and respondent behavior. Understanding the nature of polling bias is crucial for ensuring the reliability of polling data.
In the context of atlas intel polling bias, the focus is on identifying and addressing biases that may affect the accuracy of polling results. By recognizing these biases, researchers and decision-makers can take steps to minimize their impact and improve the quality of data collected.
Types of Polling Bias
- Sampling Bias: Occurs when the sample selected for polling does not accurately represent the population being studied.
- Nonresponse Bias: Happens when individuals who do not respond to a poll differ significantly from those who do, leading to skewed results.
- Question Wording Bias: Arises when the phrasing of questions influences respondents' answers, affecting the validity of the data.
- Order Effect Bias: Occurs when the order of questions affects respondents' answers, leading to inconsistencies in the data.
Causes of Atlas Intel Polling Bias
Several factors contribute to atlas intel polling bias, including methodological flaws, respondent behavior, and external influences. Understanding these causes is essential for developing strategies to mitigate bias and improve data accuracy.
Methodological Flaws
Flaws in the polling methodology can lead to significant biases. For example, using an outdated sampling frame or relying on convenience sampling can result in a sample that does not accurately represent the population. Additionally, inadequate sample size or improper weighting can further exacerbate bias.
Respondent Behavior
Respondents' behavior can also introduce bias into polling data. Social desirability bias, where respondents provide answers they believe are socially acceptable rather than truthful, is a common issue. Similarly, acquiescence bias, where respondents tend to agree with statements regardless of their actual opinions, can distort results.
External Influences
External factors, such as media coverage or political events, can influence respondents' perceptions and, consequently, their answers. These influences can lead to temporary shifts in public opinion that may not reflect long-term trends.
Read also:Laura Loomer Before Plastic Surgery Unveiling The Journey Of Transformation
The Impact of Atlas Intel Polling Bias on Data Accuracy
Polling bias can have significant implications for data accuracy, affecting the reliability of polling results and the decisions based on them. Inaccurate data can lead to flawed conclusions, potentially resulting in poor decision-making. For example, in political polling, biased results can mislead candidates and voters, affecting election outcomes.
In the business context, polling bias can lead to incorrect market predictions, affecting product development and marketing strategies. Therefore, it is crucial to address polling bias to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data.
Case Studies of Polling Bias
- 2016 U.S. Presidential Election: Many polls predicted a victory for Hillary Clinton, but Donald Trump won the election. This discrepancy was attributed to various biases, including sampling errors and nonresponse bias.
- 2019 UK General Election: Polls underestimated the Conservative Party's lead, highlighting the challenges of accurately predicting election outcomes.
Strategies to Mitigate Atlas Intel Polling Bias
To improve the accuracy of polling data, researchers can employ several strategies to mitigate atlas intel polling bias. These strategies include refining sampling methods, improving question design, and accounting for respondent behavior.
Refining Sampling Methods
Using random sampling techniques and ensuring a representative sample can help reduce sampling bias. Additionally, adjusting for demographic factors such as age, gender, and geographic location can improve the accuracy of polling results.
Improving Question Design
Carefully crafting questions to avoid leading or ambiguous language can minimize question wording bias. Pretesting questions with a small sample can also help identify potential issues before conducting a full-scale poll.
Accounting for Respondent Behavior
Recognizing and addressing respondent behavior, such as social desirability bias and acquiescence bias, can improve the reliability of polling data. Using anonymous surveys and providing clear instructions can encourage respondents to provide honest answers.
The Role of Technology in Reducing Atlas Intel Polling Bias
Advancements in technology offer new opportunities to reduce atlas intel polling bias. Online surveys, mobile polling, and data analytics tools can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of polling processes. However, these technologies also introduce new challenges, such as digital divide issues and potential biases in online sampling.
Online Surveys
Online surveys can reach a broader audience and reduce costs associated with traditional polling methods. However, ensuring a representative sample in online surveys requires careful consideration of internet access and digital literacy.
Data Analytics
Data analytics tools can help identify and correct biases in polling data. By analyzing patterns and trends, researchers can adjust for potential biases and improve the accuracy of results.
Statistical Methods for Addressing Atlas Intel Polling Bias
Statistical techniques play a crucial role in addressing atlas intel polling bias. Weighting adjustments, regression analysis, and other methods can help correct for biases in the data. These techniques require a strong understanding of statistical principles and careful application to avoid introducing new biases.
Weighting Adjustments
Weighting adjusts the sample to match the population's demographic characteristics, reducing bias caused by underrepresented groups. However, improper weighting can lead to overcorrection and other issues.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis can identify relationships between variables and adjust for potential biases in the data. This method requires a robust dataset and careful interpretation of results.
Best Practices for Conducting Polls
To minimize atlas intel polling bias, researchers should follow best practices in conducting polls. These practices include clearly defining objectives, using appropriate sampling methods, and ensuring transparency in data collection and analysis.
Defining Objectives
Clearly defining the objectives of a poll helps ensure that the methodology and questions align with the research goals. This clarity can improve the accuracy and relevance of the data collected.
Ensuring Transparency
Transparency in data collection and analysis builds trust with stakeholders and allows for independent verification of results. Providing detailed information about the methodology, sample characteristics, and data analysis can enhance the credibility of polling results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, atlas intel polling bias poses significant challenges to the accuracy and reliability of polling data. By understanding the causes and types of bias, researchers and decision-makers can take steps to mitigate its effects and improve data quality. Employing best practices, leveraging technology, and using statistical methods are essential strategies for addressing polling bias.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with polling bias in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into data analysis and decision-making. Together, we can work towards more accurate and reliable polling data, leading to better-informed decisions.
Table of Contents
- What is Polling Bias?
- Types of Polling Bias
- Causes of Atlas Intel Polling Bias
- The Impact of Atlas Intel Polling Bias on Data Accuracy
- Strategies to Mitigate Atlas Intel Polling Bias
- The Role of Technology in Reducing Atlas Intel Polling Bias
- Statistical Methods for Addressing Atlas Intel Polling Bias
- Best Practices for Conducting Polls
- Case Studies of Polling Bias
- Conclusion